“Hindoustan ou Inde” has been added to your cart.
View cart
-
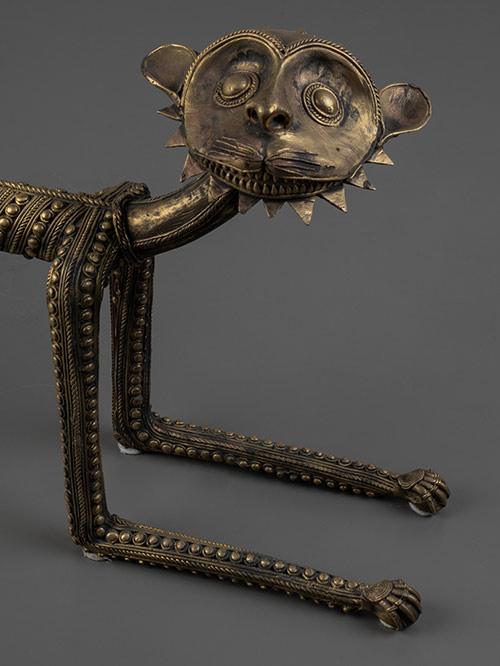
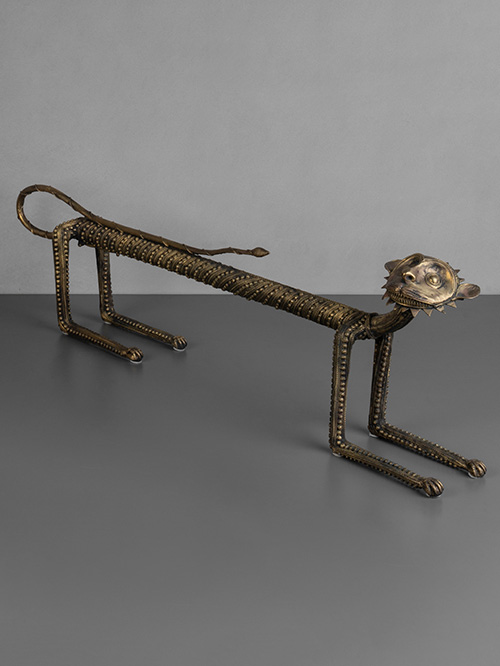


Bastar (Chhattisgarh, Central India)
Brass, Dokra work
The tiger is the vehicle of, and sacred to, Danteshwari Mata who is a form of the powerful Goddess Durga and is also the family goddess of the princes of Bastar.
Suresh Waghmare (signed)
Born in 1970 in a Maharashtrian family in Bastar district, he began to study the technique of Bell Metal Casting with Guru Phool Singh Bisara when he was twelve. Since then he has been working as a member of the co-operative of craftsmen. He is a master craftsman in the art of metal casting and has participated in many international exhibitions.
Size (cms): 29.5(H) x 106(W) x 11(D)
Size (inches): 11.5(H) x 41.5(W) x 4.5(D)
-
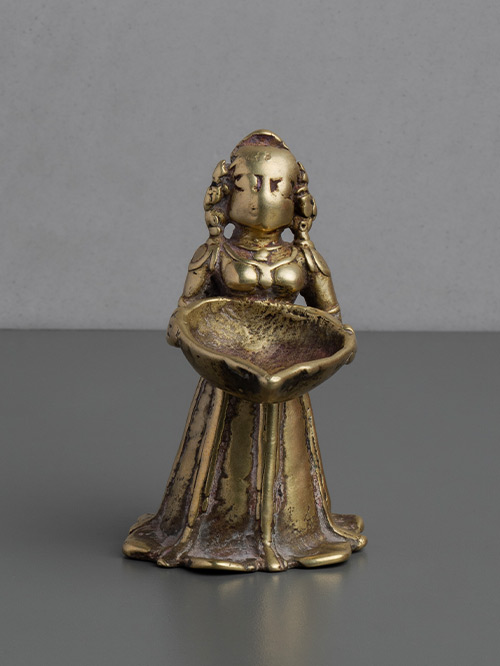
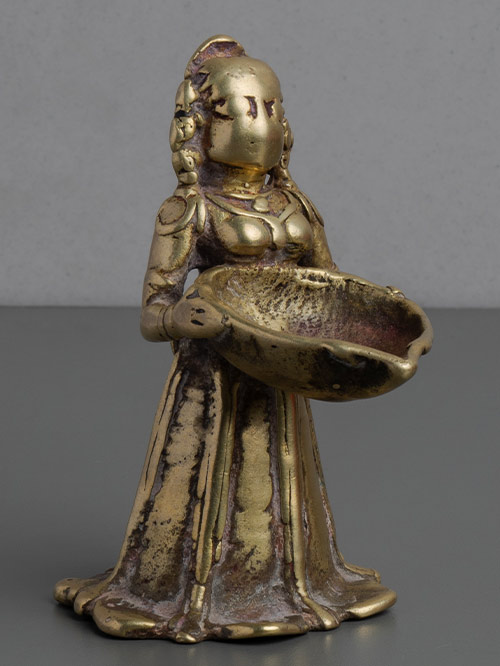


Karnataka
Brass alloy
This attractive and patinated Lakshmi of diminutive proportions stands proudly, holding a deep reservoir burner in her outstretched hands. She wears a long, flowing skirt that touches the floor. Her features, once delicately carved, have been partially worn by years of ritual use. Her hair is tied in a long braid that hangs along her back.
Dipalakshmi or Deepalakshmi is identifiable with Lakshmi, the Goddess of light and wealth. Dipalakshmi is usually shown holding the lamp bowl in her hands cupped in the gesture of anjali or offering of the flame of ‘divine light’ which, when lit kindles light into the image. The lamp is conceived as the vehicle through which the divine can be accessed. Lamps are used in rituals within the domestic realm, as well as religious or temple settings, in order to propitiate the gods.
Size (cms): 9.5(H) x 6(W) x 7.5(D)
Size (inches): 3.5(H) x 2.5(W) x 3(D)
-
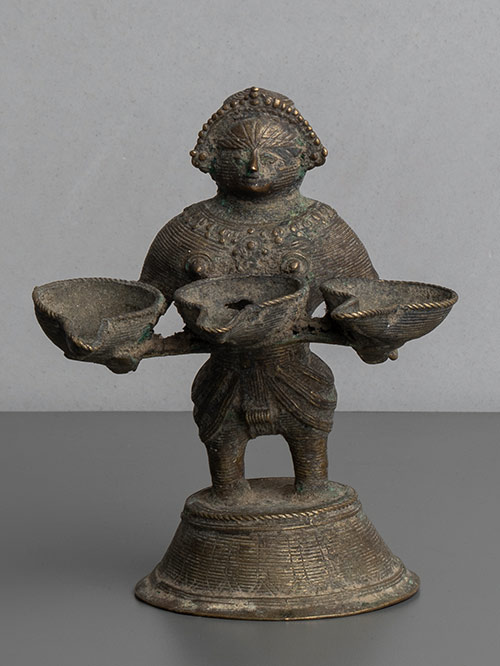
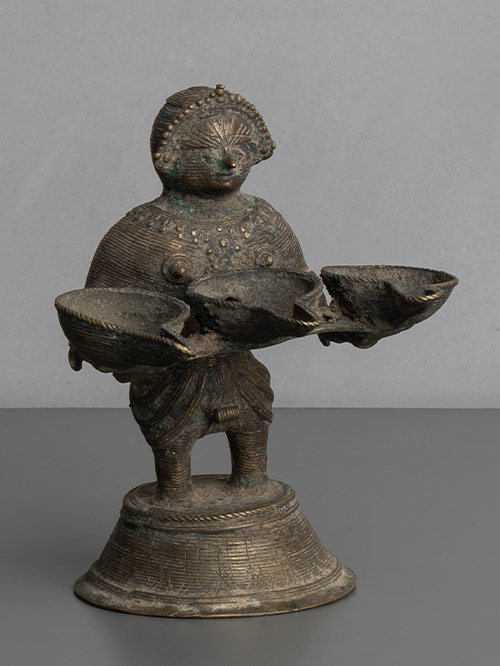


Bastar (Chhattisgarh, Central India)
Brass, Dokra work
An unusual Dipalakshmi lamp from the Bastar region, in the form of a female figure standing holding three teardrop-shaped lamp bowls in her hands. The fine cross-hatching and details are typical of Bastar casting. Dipalakshmi, the Goddess of light and wealth, is usually shown holding the lamp bowl in her hands cupped in the gesture of anjali or offering of the flame of ‘divine light’ which, when lit, kindles light into the image.
Dhokra is non–ferrous metal casting using the lost-wax casting technique. This sort of metal casting has been used in India for over 4,000 years and is still used. One of the earliest known lost wax artefacts is the dancing girl of Mohenjo-Daro. The product of dhokra artisans is in great demand in domestic and foreign markets because of primitive simplicity, enchanting folk motifs and forceful form. Dhokra horses, elephants, peacocks, owls, religious images, measuring bowls, and lamp caskets, etc., are highly appreciated.
Size (cms): 14(H) x 12(W) x 12.5(D)
Size (inches): 5.5(H) x 4.5(W) x 5(D)
-
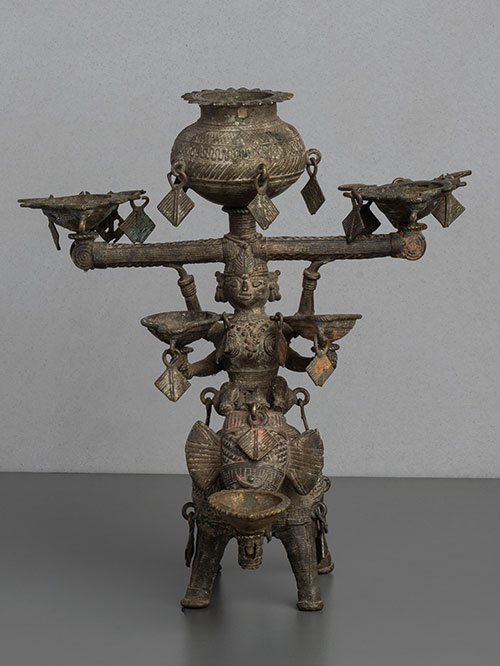
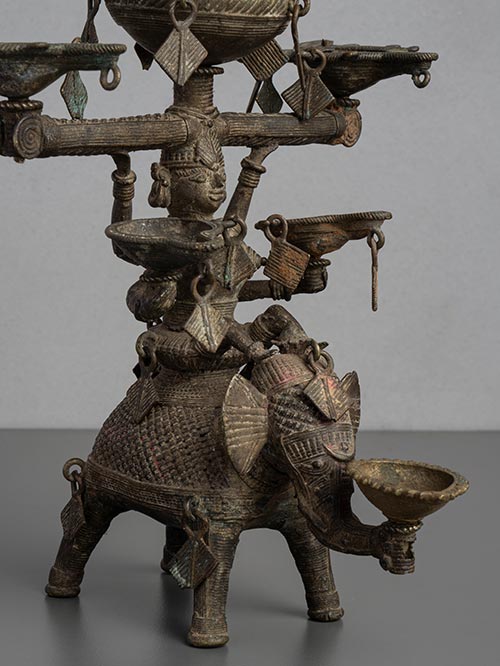


Bastar (Chhattisgarh, Central India)
Brass, Dokra work
An oil lamp depicting Panchdipa, the Goddess of Light who is depicted riding an elephant and bearing a kalasha, or pitcher for oil, on her head. The Goddess also provides support to four oil burners and the elephant holds an additional burner with his trunk. The fine cross-hatching and details are typical of Bastar casting.
Dhokra is non–ferrous metal casting using the lost-wax casting technique. This sort of metal casting has been used in India for over 4,000 years and is still used. One of the earliest known lost wax artefacts is the dancing girl of Mohenjo-Daro. The product of dhokra artisans is in great demand in domestic and foreign markets because of primitive simplicity, enchanting folk motifs and forceful form. Dhokra horses, elephants, peacocks, owls, religious images, measuring bowls, and lamp caskets, etc., are highly appreciated.
Size (cms): 23(H) x 21(W) x 17(D)
Size (inches): 9(H) x 8.5(W) x 6.5(D)
-
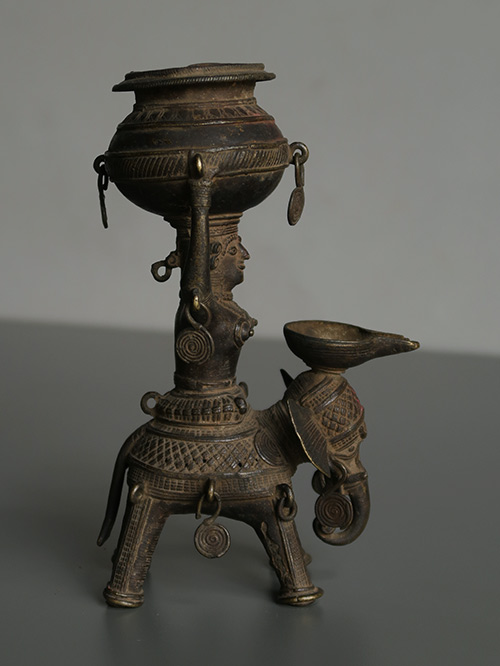
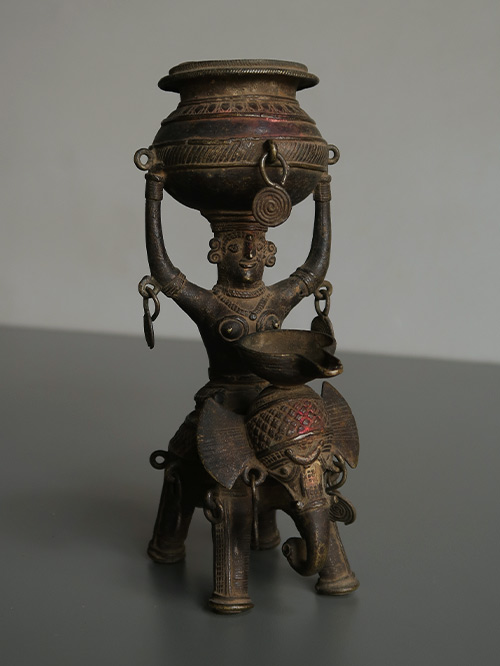


Bastar (Chhattisgarh, Central India)
Brass, Dokra work
An oil lamp depicting Panchdipa, the Goddess of Light who is depicted riding an elephant and bearing a kalasha, or pitcher for oil, on her head. The Goddess and elephant also provide support to a singular oil burner. The fine cross-hatching and details are typical of Bastar casting.
Dhokra is non–ferrous metal casting using the lost-wax casting technique. This sort of metal casting has been used in India for over 4,000 years and is still used. One of the earliest known lost wax artefacts is the dancing girl of Mohenjo-Daro. The product of dhokra artisans is in great demand in domestic and foreign markets because of primitive simplicity, enchanting folk motifs and forceful form. Dhokra horses, elephants, peacocks, owls, religious images, measuring bowls, and lamp caskets, etc., are highly appreciated.
Size (cms): 20(H) x 12.5(W) x 8.3(D)
Size (inches): 8(H) x 5(W) x 3.5(D)
-
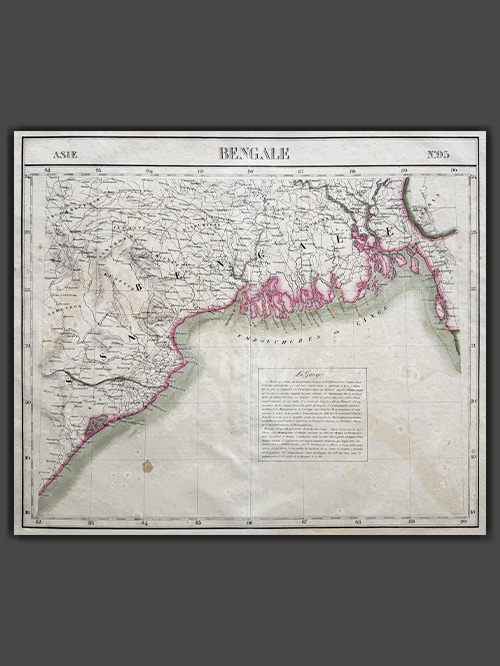
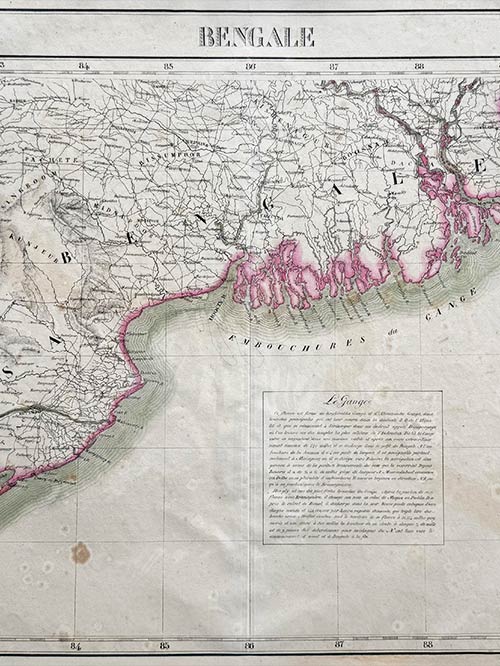
Original lithographed map by Philippe Vandermaelen (1795-1869)
An attractive map from Atlas Universel de Geographie depicts parts of present-day Bangladesh, Bihar, Orissa, West Bengal, and Tripura. This atlas was groundbreaking as the first to present all maps on a uniform scale of 1:1,641,836, with each map covering approximately 20 degrees of longitude (from Paris) and 6 degrees of latitude. Published between 1825 and 1827 in a single edition with 810 copies sold, it offered unprecedented detail for many regions, particularly the American West. The maps were hand-painted in outline colour, showcasing remarkable craftsmanship.
Philippe Marie Guillaume Vandermaelen (1795–1869), the Flemish cartographer behind this monumental work, was a native of Brussels and initially trained as a globe maker. His innovative vision of mapping on a universal scale was likely influenced by this early training. Beyond the Atlas Universel, Vandermaelen created globes, regional maps, a 250-sheet map of Belgium, and other significant works, establishing himself as a key figure in 19th-century cartography.
Image Size (cms): 49.5(H) x 57(W)
Image Size (inches): 19.5(H) x 22.5(W)
-
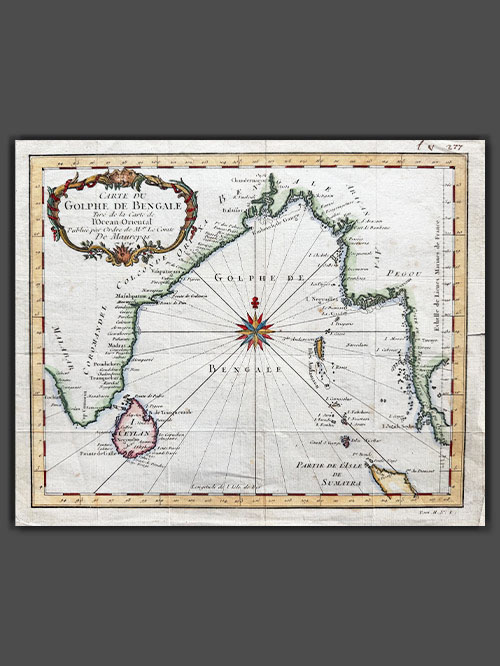

Original engraved plan by Jacques Nicholas Bellin (1703-1772)
This exquisite map by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin illustrates the Bay of Bengal during the height of French influence in India. Published in 1740, the map showcases coastal cities, islands, and regions of strategic and economic importance during a period when France nearly rivaled Britain as the dominant European power on the subcontinent.
The map highlights key coastal cities along the Bay of Bengal, including Pondicherry (Pondicheri) marked with a star, the capital of French India, which was central to French administration and trade. While overshadowed by British dominance, France’s influence in India was notable, with territories like Pondicherry, Yanam, Mahe, and Karikal. French ambitions, driven by competition with Britain, escalated in the mid-18th century under Joseph François Dupleix, leading to conflicts like the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years’ War. Though the British defeated the French at the Battle of Plassey in 1757, France retained control of its coastal territories until India’s independence in 1947 and the formal transfer in 1962.
This map was meticulously crafted by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin and published as plate No. 1 in Volume 2 of the 1740 edition of Abbé Prévost’s L’Histoire Générale des Voyages. Bellin’s work, renowned for its precision and detail, is preserved in several libraries across Europe and North America, either as an individual map or as part of Prévost’s celebrated publication.
Image Size (cms): 23.5(H) x 28.5(W)
Image Size (inches): 9.5(H) x 11(W)
-
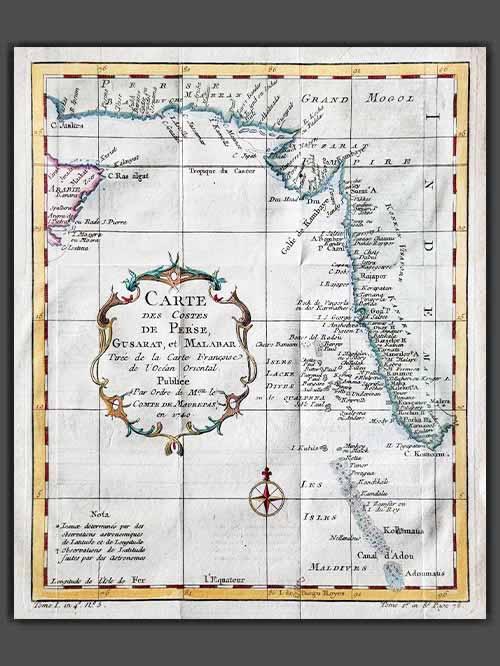
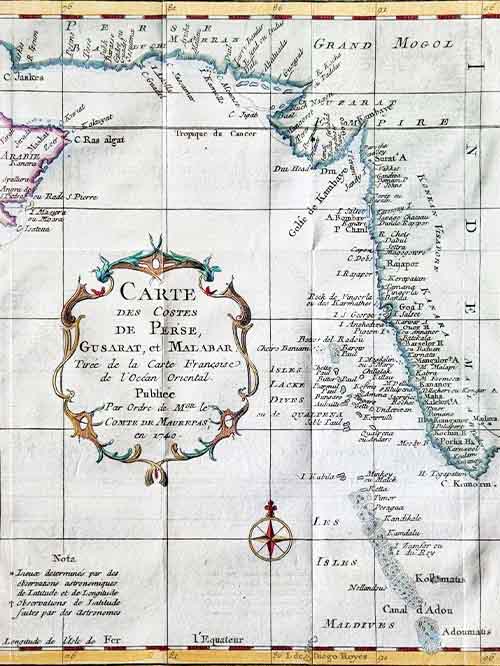
Original engraved plan by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin (1703–1772)
This decorative engraved map by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin appears in Abrégé de l’histoire générale des voyages, published in Paris in 1780. It depicts the region from the mouth of the Persian Gulf to the Maldives, showcasing all major ports and towns along this strategically significant area.
Jacques-Nicolas Bellin was a pivotal figure in 18th-century cartography, serving as Hydrographer to the French Navy and the first Ingénieur Hydrographe at the French Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine. Over a 50-year career, Bellin produced hundreds of maps and charts celebrated for their accuracy and functionality, setting a high standard in European cartography. His works included major sea atlases such as Neptune François (1753), Hydrographie Française (1756), and the comprehensive Petit Atlas Maritime (1764), featuring 580–581 finely detailed charts. Bellin also contributed extensively to Diderot’s Encyclopédie and Abbé Prévost’s Histoire Générale des Voyages. A child of the Enlightenment, Bellin prioritized scholarly precision and cited his sources diligently, distinguishing his work from the more decorative styles of earlier mapmakers. His contributions cemented France’s dominance in cartography and influenced his student, Rigobert Bonne, who succeeded him at the Dépôt.
Image Size (cms): 26(H) x 21(W)
Image Size (inches): 10(H) x 8.5(W)
-
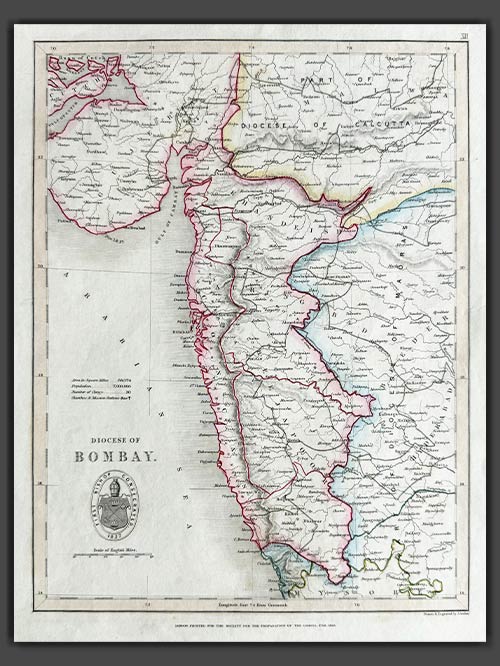
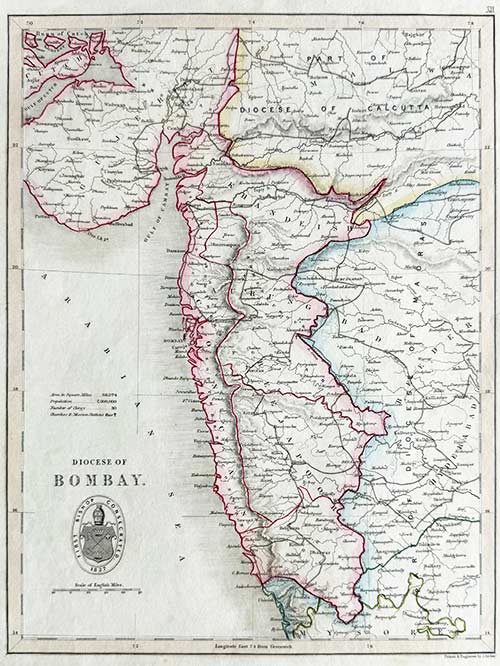
Original engraved map by J. Archer
from The Colonial Church Atlas
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bombay is one of the most prominent Catholic jurisdictions in India, serving as the metropolitan see for the province of Bombay. Established as a vicariate in 1637 and elevated to an archdiocese in 1886, it encompasses Bombay and its surrounding areas. The Cathedral of the Holy Name in Colaba stands as its mother church.
The archdiocese is central to the spiritual, educational, and social fabric of the region’s Catholic community. Its extensive network includes parishes, schools, colleges, hospitals, and charitable organizations, which cater to people of all faiths. Known for its cultural and liturgical events, the Archdiocese of Bombay reflects the vibrancy and diversity of Mumbai’s Catholic population.
Size (cms): 30.5(H) x 23(W)
Size (inches): 12(H) x 9(W)
-
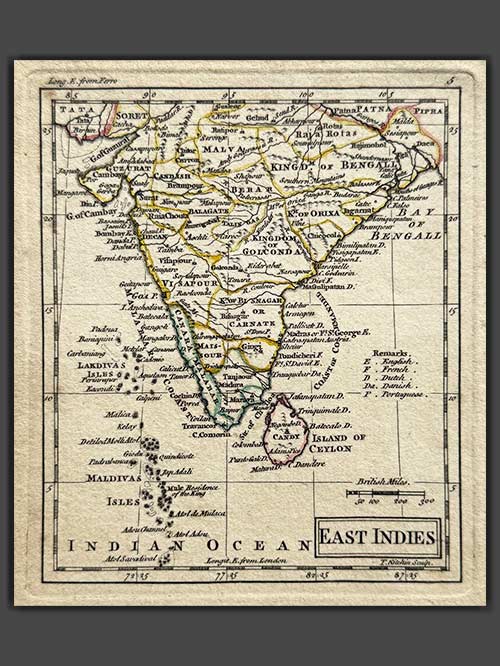
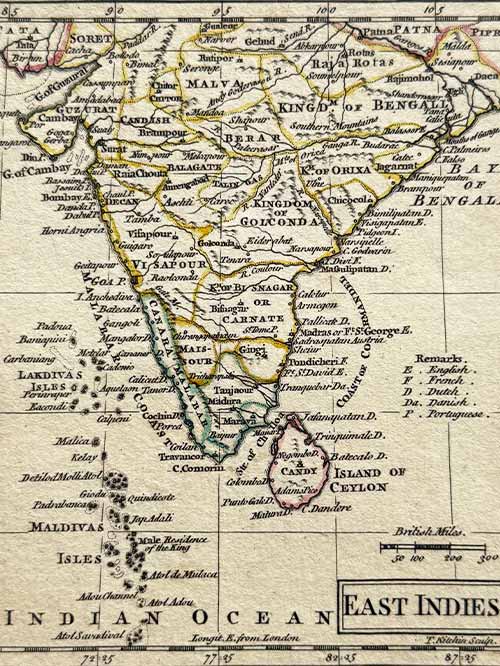
Original engraved map by A Dury (1766-1777)
This original, rare map of India, engraved by A. Dury (fl. 1766–1777), was published in 1761 as part of the A New General and Universal Atlas.
Dury was a British map and print publisher based in Duke’s Court on St. Martin’s Lane in London. Although he was a skilled mapmaker, he achieved less success than his contemporaries, such as Thomas Jefferys and William Faden, making his maps relatively rare. Dury is most commonly associated with the large Indian maps by James Rennell, one of his key collaborations. In addition, he produced notable maps during the Revolutionary War, including plans of Boston and Philadelphia, as well as a series related to the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–74. Despite his limited commercial success, Dury’s works remain valuable for their historical and cartographic significance.
Size (cms): 14.5(H) x 12.5(W)
Size (inches): 5.5(H) x 5(W)
-


Bhil Tribes (Central India)
by Bhuri Bai
watercolour on canvas
Bhuri Bai grew up in the Jhabua district on the Madhya Pradesh-Gujarat border. J Swaminathan identified her as a potential artist nearly three decades ago, when she was a 20-year-old daily wage labourer. She picks up clues from the arts of embroidery as well as ritual narratives; her images shuttle between the intimate and the cosmic. This is especially evident in paintings where she depicts stags whose antlers grow into forests, their bodies distinctively patterned after desert dunes or river wavelets. She returns, often, to variations on the Tree of Life motif, playfully annotating its mythic presence with owls that stand on stilt-legs, timid snakes, and high-spirited elephants. Bhuri Bai demonstrates a lively and witty eye for observed detail, veining her observations with allegorical or parabolic intent.
Painting Size (cms): 74(H) x 54(W)
Painting Size (inches): 29(H) x 21.5(W)
Framed Size (cms): 79(H) x 59(W)
Framed Size (inches): 31(H) x 23(W)
-
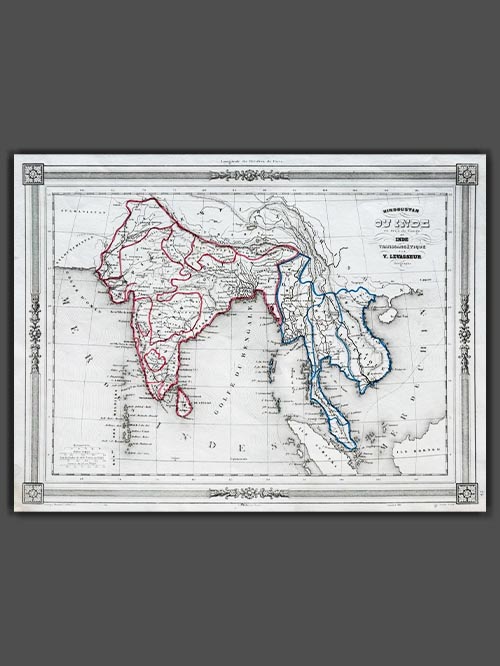
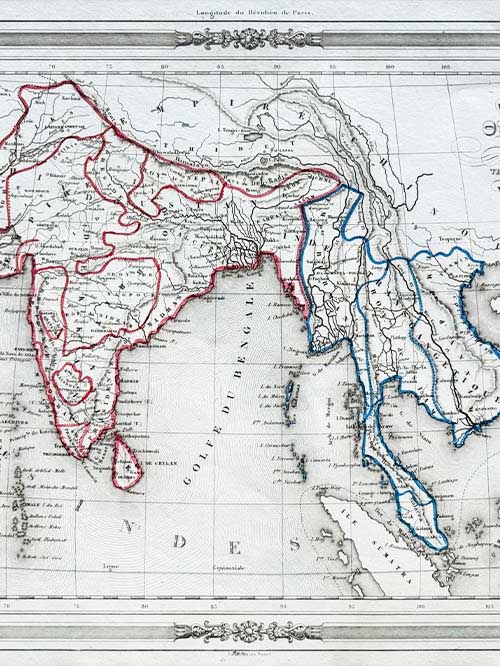
Original engraved map by V. Levasseur ( 1800-1870)
Victor Levasseur’s 1848 map of India and Southeast Asia, created for Maison Basset’s Atlas Illustré destiné à l’enseignement de la géographie élémentaire, offers a detailed and visually captivating depiction of the Indian subcontinent and surrounding regions. This finely engraved map provides extensive coverage of key areas, including India, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and the islands of Borneo and Sumatra.
Victor Levasseur was a renowned French engineer, cartographer, and engraver who made significant contributions to 19th-century cartography. He held several important political and educational positions related to cartography in France. Levasseur is best known for his Atlas National Illustré des 86 Départements et des Possessions de La France, a highly decorative atlas that includes his Planisphere and five notable continental maps.
Size (cms): 24.5(H) x 32.5(W)
Size (inches):9.5(H) x 13(W)
-
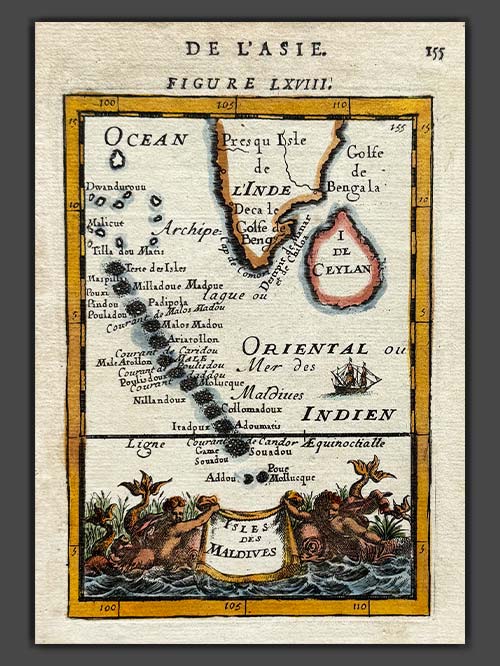
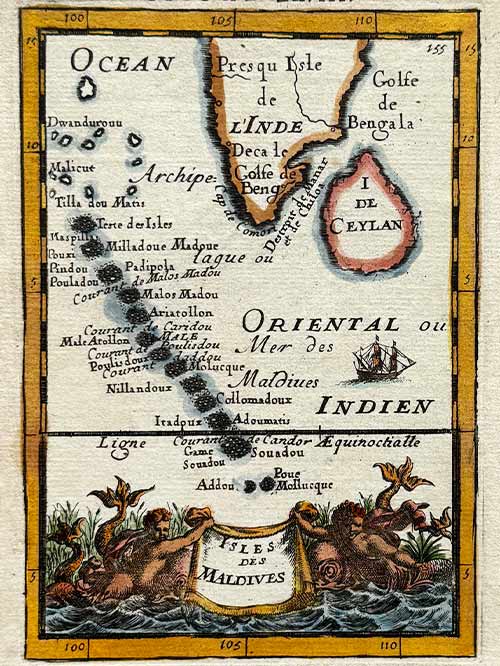
Original engraved map by A.M. Mallet (1630-1706)
This detailed map of the Maldives, southwest of the southern tip of India, showcases excellent detail and features a decorative title cartouche and vignette at the bottom. It originates from Mallet’s monumental Description de L’Univers, first published in Paris in 1683, regarded as one of the greatest works of its kind in the 17th century.
Alain Manesson Mallet (1630–1706), a French cartographer and engineer, began his career as a soldier in the army of Louis XIV, later becoming a Sergeant-Major in the artillery and an Inspector of Fortifications. He also served under the King of Portugal before returning to France, where he was appointed to the court of Louis XIV and taught mathematics. Mallet’s major publications include Description de L’Univers (1683) in five volumes, from which this map originates, and Les Travaux de Mars ou l’Art de la Guerre (1684) in three volumes.
Description de L’Univers encompasses a wide range of information, including star maps, maps of both the ancient and modern worlds, and a summary of the customs, religions, and governments of various nations. It is suggested that Mallet’s teaching background influenced his focus on entertaining readers, as reflected in the charming harbour scenes and rural landscapes he included beneath his descriptions of astronomical concepts and diagrams. Most of the figures engraved for this work were drawn by Mallet himself.
Size (cms): 17.5(H) x 13.5(W)
Size (inches): 7(H) x 5.5(W)
-
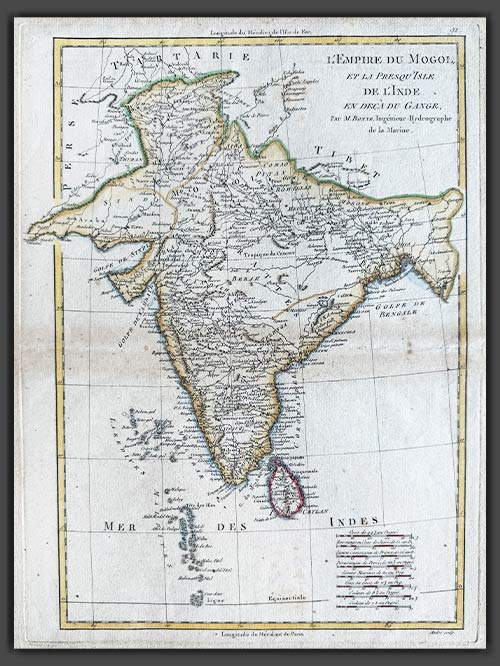
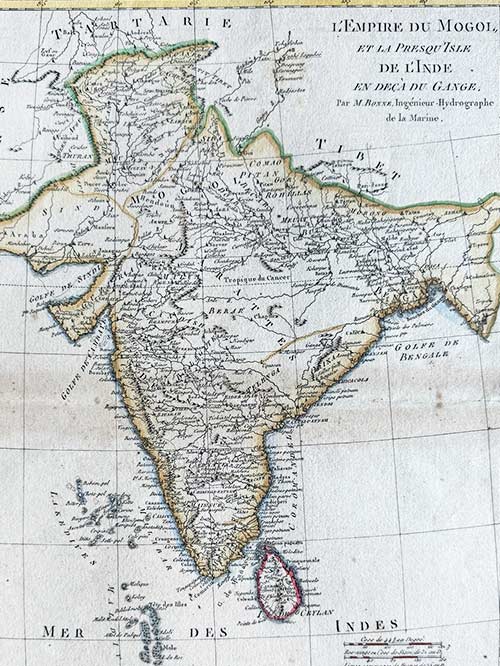
SOLD
Original engraved map by Rigobert Bonne (1727-94)
This original copper-plate engraved map of India from the Mogul Empire in the north to the Ganges and south to Ceylon was published in Paris for the Atlas Supplement, circa 1787.
Bonne was a renowned French cartographer, recognised as one of the most significant figures in cartography during the late 18th century. In 1773, he succeeded Jacques Nicolas Bellin as Royal Cartographer to France, serving as Hydrographer at the Dépôt de la Marine. In this role, Bonne produced some of the most detailed and accurate maps of his era. His work marked a shift in cartographic style, moving away from the decorative designs of the 17th and early 18th centuries toward a more practical and detail-oriented approach. While retaining stylistic similarities to Bellin in terrain depiction, Bonne’s maps typically omitted decorative features like elaborate cartouches, hand coloring, and compass roses. Primarily focused on coastal regions, Bonne’s maps are highly esteemed for their precision, historical value, and aesthetic simplicity.
Image Size (cms): 37(H) x 27(W)
Image Size (inches): 14.5(H) x 10.5(W)
-
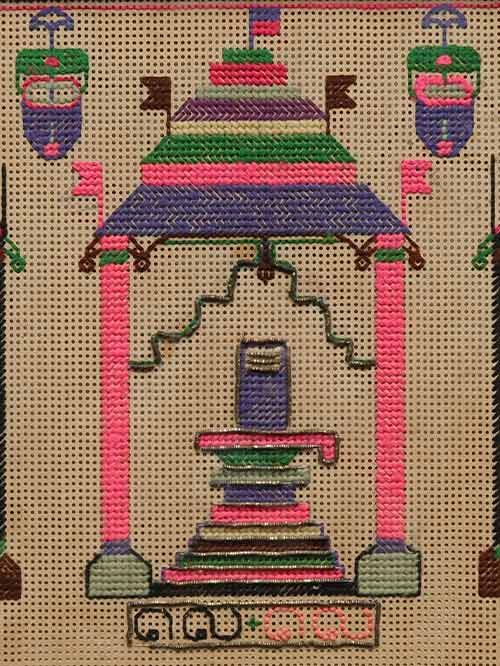


Chettinad (Tamil Nadu)
cross stitch embroidery
This decorative cross stitch embroidery artwork depicts three pillared niches, the central larger one with lingam flanked by two smaller ones with Ganesha and Kartikeya, temple lamps suspended above.
Framed Size (cms): 32(H) x 49(W)
Framed Size (inches): 12.5(H) x 19.5(W)
-


Rajasthan
Opaque watercolour on cloth with highlights in gold
Size (cms): 136(H) x 68(W)
Size (inches): 53.5(H) x 27(W)

































