“Krishna and Yashoda” has been added to your cart.
View cart
-
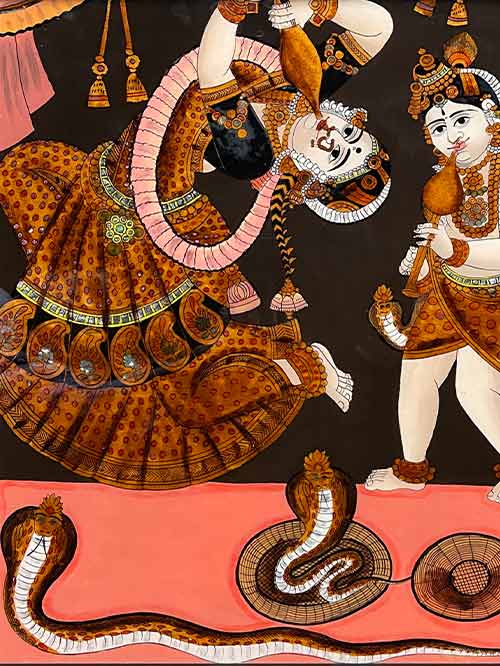


Tanjore (South India)
reverse painting on glass
A charming reverse glass painting depicting a Krishna and Yashoda as snake charmers each hypnotising a cobra with the melodic sounds of their fluted instruments called pungis. The adolescent Krishna is bejewelled and splendidly clad in a lower garment with a hip-hugging sash and a garland of flowers around his neck. His foster-mother Yashoda who is also gorgeously robed and jewelled contorts around to befuddle the snakes.
Reverse glass paintings were introduced into India the late 18th century from China by way of the China Trade. Indian artists adopted the technique of reverse glass painting partly on account of its novelty and also because it was a relatively inexpensive medium which could produce rich effects. The technique proved extremely popular and soon spread through western and southern India and even to former provincial Mughal capitals of Oudh, Murshidabad.
In Tanjore – a small state with an old art tradition- a distinctive school of glass painting developed in the early 19th century and continued for more than a hundred years. The style was essential Indian – it tended to repeat patterns of regional painting: images of deities, portraits and themes form the ancient myths, secular themes such as portraits of kings or nobles, courtesans and musicians. The colour was rich and the style bold and defiant. The subjects were clearly presented with a certain opulence and glamour.
Painting Size(cms): 47 (H) x 43.2 (W)
Painting Size(inch): 18.5 (H) x 17 (W)
Framed Size (cms): 49.5(H) x 46(W)
Framed Size (inches): 19.5(H) x 18(W)
-


Tanjore (South India)
reverse painting on glass
Krishna as a child lies on a giant banyan leaf content, innocent, with a hint of amusement on his face. Naked but for his jewellery and a draped angavastra, he is depicted sucking his raised toe. As always, he is shown as a chubby child. The leaf he rests on is encircled by a school of fish, swimming amidst the primordial waters. Depicted on the top right is the sage Markandeya reaching out for the safety of the banyan leaf. A diminutive Brahma hovers above Krishna’s left foot. A border of leaves and roundels frames the scene.
The story of Krishna as Vatapatrasayi, or the Lord of the Banyan Leaf, occurs during the end of the world when the sage Markandeya sees the destruction caused by the great flood. In the midst of the chaos, he sees a small child floating on a banyan leaf, sucking his raised toe. Markandeya is drawn into the child’s body where he discovers the entire world, with all its realms, contained within the child who is oblivious to the disaster happening outside. The sage then realises that the child is a god who has taken the world into himself before recreating the universe.
Reverse glass paintings were introduced into India the late 18th century from China by way of the China Trade. Indian artists adopted the technique of reverse glass painting partly on account of its novelty and also because it was a relatively inexpensive medium which could produce rich effects. The technique proved extremely popular and soon spread through western and southern India and even to former provincial Mughal capitals of Oudh, Murshidabad. In Tanjore a distinctive school of glass painting developed, with a rich colour and bold and defiant style. The subjects were clearly presented with a certain opulence and glamour.
Framed Size (cms): 46.5(H) x 41.5(W)
Framed Size (inches): 18.5(H) x 16.5(W)
Painting Size (cms):39.5(H) x 31.5(W)
Painting Size (inches):15.5(H) x 12.5(W)
-
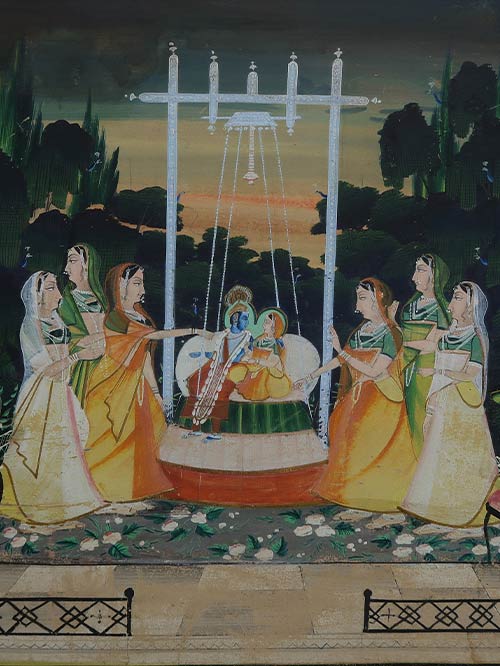
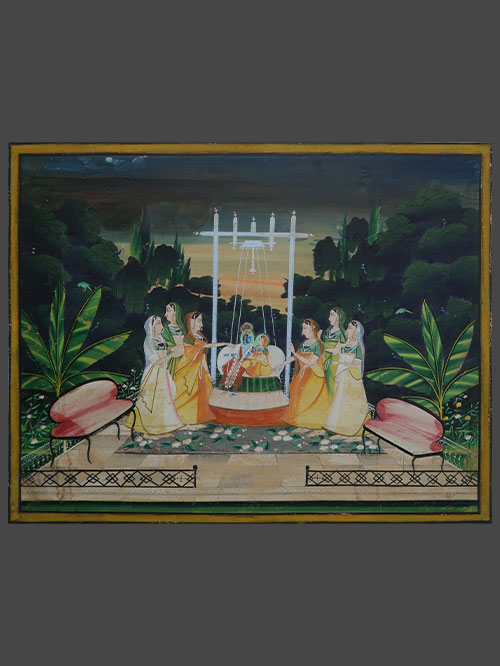


Nathdwara (Rajasthan)
opaque watercolour and gold on paper
Krishna and Radha sit resting against a large white bolster on an ornate silver swing. Underfoot is a floral decorated carpet on a chequered marble floor with iron balustrades. Six female attendants flank the nimbate couple whose gazes are firmly fixed on each other. In the foreground are a pair of European style pink settees while in the distance an orange hued sky indicates the setting sun. Dense clusters of trees and foliage sprinkled with parrots and peacocks envelope the central scene.
Such large and dramatic scenes were painted by Nathdwara artists who produced these images for devotees who visited the great Krishna temple at Nathdwara in Rajasthan. Founded in the 17th century, this temple has attracted an enormous following even to this day, in turn ensuring a continuing tradition of devotional images. The extravagant size and conception of these paintings remind one of the constant importance of religious images in India, not only as ritual objects but also items for pilgrims to acquire and bring home from the great Hindu shrines.
Towards the end of the nineteenth century and early twentieth century Nathdwara artists were exposed for the first time to European art prints whose influence can be seen in the paintings of this period.
Size Painting (cms): 44.5 (H) x 57 (W)
Size Painting (inch): 17.5 (H) x 22.4 (L)
-
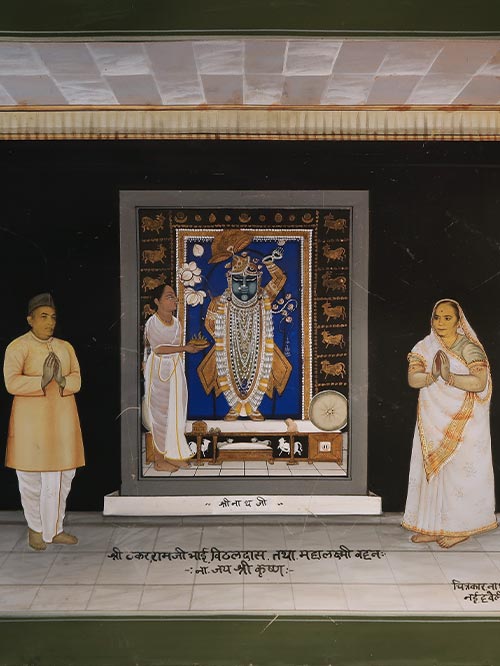
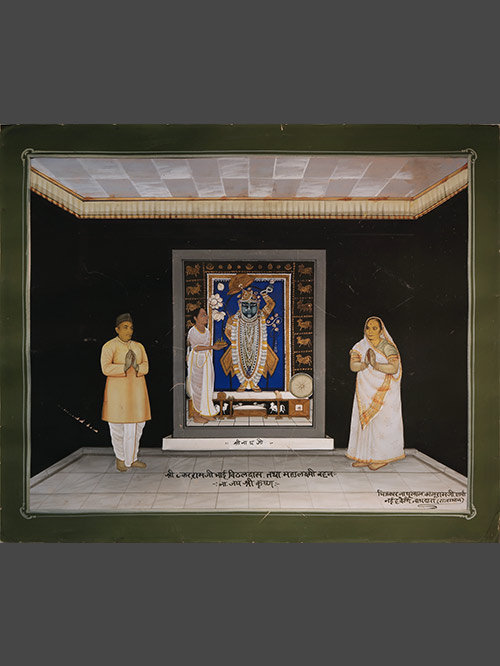


Nathdwara (Rajasthan)
Opaque watercolour, gold and gelatin silver print on paper
Inscribed on recto ‘Nathulal Kaluramji Sharma, Nathdwara’
In Pushti Marga terminology, to perform a manoratha is to offer a seva ( ritualistic service) to the deity in fulfilment of a long cherished inner yearning to serve him in a special way on a particular day. Only a few select Goswamis, direct descendants of Vallbhacharya, are given this privilege and every Goswami longs to perform a manoratha at least once in a lifetime. A wealthy devotee can also perform a manoratha on an important day of his life or in the fulfilment of a vow. This is done by contributing towards the expenses of a particular darshana ( formal viewing of a deity) or by paying for the seva of an entire day. To commemorate this event, devotees usually commission a painting showing them on both sides of Srinathji outside the threshed of the sanctum. In the present painting actual photographs of the donors faces are incorporated into the painting. This served as a visual record of their worship before the famed icon.
Sri-Nathji ( The Lord of Shri, Goddess of Wealth) enshrined at Nathdwara is the most important svarupa (own form) in the Pushti Marga, and represents Krishna at the age of seven. Sri-Nathji is Krishna incarnate, the tutelary deity of the Vallabhacharya whose swarupa or image is enshrined at Nathdwara.
Painting Size (cms): 50.5 (H) x 60.5 (L)
Painting Size (inch): 19.9 (H) x 23.8 (L)
-
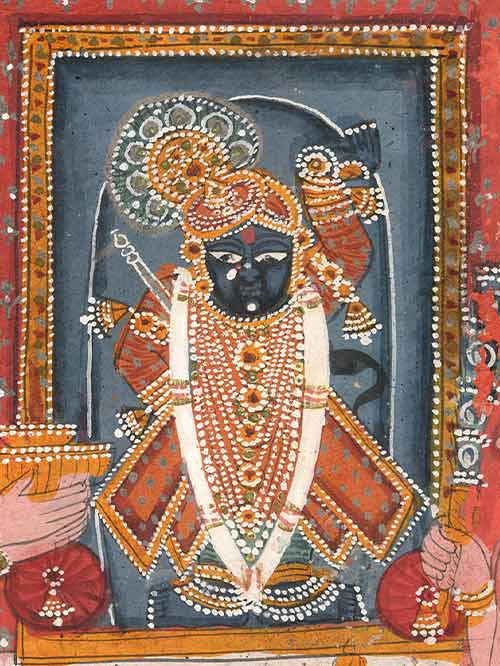


Nathdwara (Rajasthan)
Opaque pigments on paper
Srinathji wears a Chakdarwagha (coat with four pointed ends) with pyjama (trousers), a mustard upper garment, and a bejewelled raj mukuta or regal fan-shaped turban ornament. His left hand is raised to symbolize the lifting of the sacred mountain Govardhana, and he holds his cowherd’s stick (lakut). At his feet are two folded betel leaves and the jhari or covered pot of Jumna water, symbolising the ever-present love of his foster-mother Yashoda. Tilkayat Govindji and his young son Girdharji are seen on either side of Srinathji, the former carrying an arti lamp and the latter a peacock whisk. A chequered mauve and blue carpet lies underfoot, with a floral saffron pichhwai behind the deity and overhanging crimson curtains.
Painting Size (cms): 24(H) x 17(W)
Painting Size (inches): 9.5(H) x 6.5(W)
-
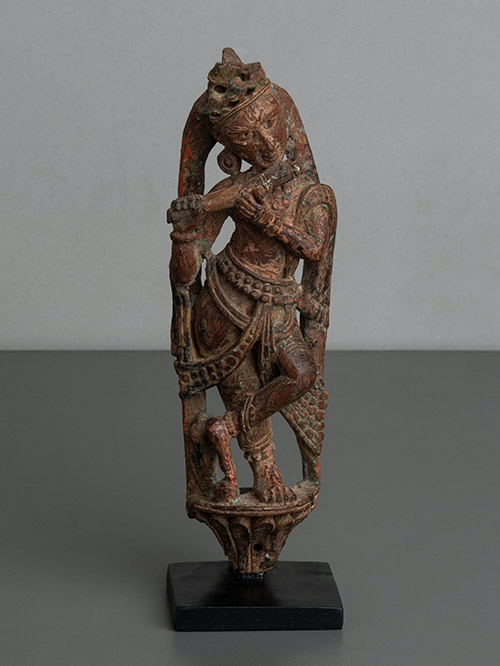
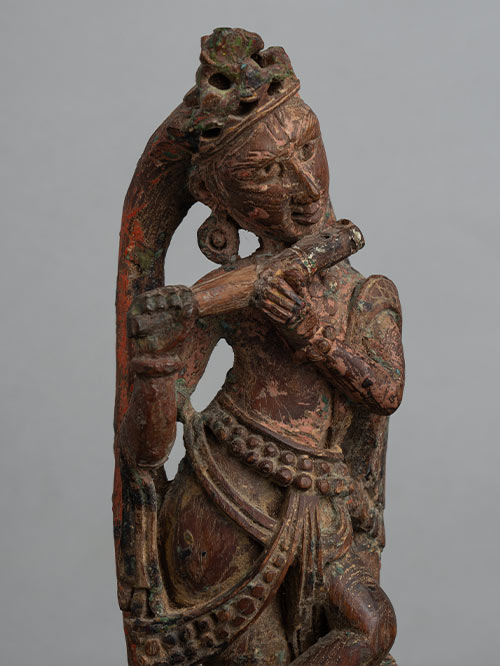


Gujarat
Wood with traces of polychroming
One of the most abiding images in Indian art is that of Krishna the flautist standing with his legs crossed at the ankles and playing the flute. He wears a decorative mukuta or crown, a dhoti and various necklaces, bangles and anklets.
The image of Venugopala rather late in Indian literature and art and it has been suggested that the classical myth of Orpheus may have exerted some influence. The idea derives from the lonely shepherd who plays his bamboo flute (venu) while tending his flock. While other cowherders f Braj hold a shepherd’s staff, Krishna’s staff is also his flute. He, however does not play upon it to please the cows, but to charm the gopis or cowherdesses
Size (cms): 24(H) x 7.5(W) x 6.5(D)
Size (inches): 9.5(H) x 3(W) x 2.5(D)
-
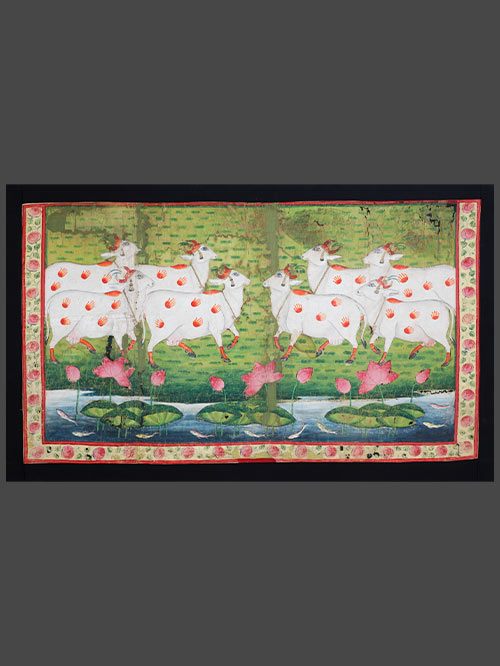


Nathdwara (Rajasthan)
Cotton, painted on pigments
An attractive small Pichhwai depicting eight white cows grouped in a meadow with a lotus and fish filled stream in the foreground. The cows are bedecked and have henna on their horns and hooves. Large handprints painted in saffron henna cover bodies. A floral border surrounds the panel. This pichhwai would have either accompanied a larger pichhwai in a prominent shrine or constituted part of a small domestic shrine.
Gopashtami is a festival that commemorates Krishna’s elevation from a young herder of calves to full cowherd. Krishna grows into the perfect cowherd, the one all the cows heed, answering to the golden strains of his flute. At Nathdwara the cows, decked in their finest, are brought into the haveli. There is a playful spirit about this festival that is well expressed in this pichhwai. The cows, gentle creatures with limpid eyes and expressive ears, are constant reminders of Vraja and Krishna’s childhood occupation as cowherd.
Size (cms): 75(H) x 124(W)
Size (inches): 29.5(H) x 49(W)
-

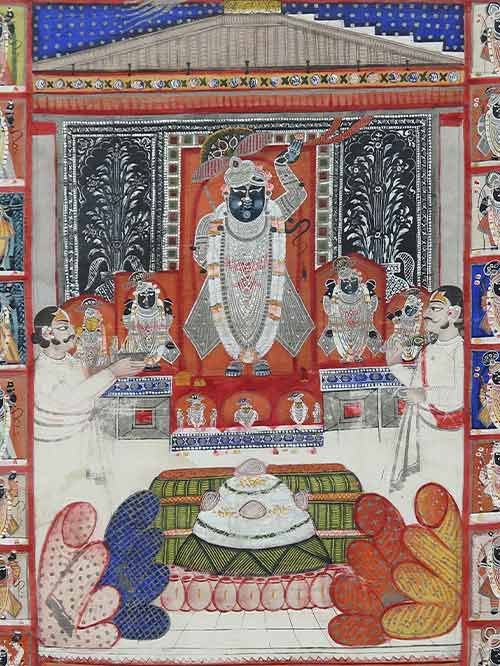
Nathdwara (Rajasthan)
Cotton, painted on pigments
A scarce small Pichhwai celebrating Sapta Swarupa Annakutotsava, with the central figure of Srinathji accompanied by his seven forms (Sapta Swarupa) and attended by two goswamis. Srinathji and the sath swarupa, are all richly adorned and bejewelled and they stand upon an elevated altar in front of a saffron covered thada vastra. A richly embroidered tree-of-life hanging encrusted with jewels and pearls is placed behind the shrine.
A veritable feast of chhappan bhoga (fifty-six offerings) in the form of large mounds of rice and curd, festooned with pink sweet meats are laid out in front of Srinathji. These offering commemorate the grand festival of Annakuta, the largest yearly festival celebrated at Nathdwara, which is held the day after Diwali. The festival is celebrated in recognition of an episode in the life of Krishna when he persuaded the villagers of Vraj to present their harvest offerings to the spirit of Mount Govardhana, instead of Indra. The mountains of rice symbolically represent Mount Govardhana which are topped by a sweet cake called gunja representing the head of Vishnu flanked by four more signifying the four ayudhyas or weapons of Vishnu.
The pichhwai is bordered by bands depicting Srinatji in twenty-four different Darshan attires on its sides and top and a row of nandis (cows) above a lotus filled lake below.
Size (cms): 81(H) x 59(W)
Size (inches): 32(H) x 23(W)

















